Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) is a common complication during pregnancy resulting from poorly controlled blood sugar levels. It is growing in prevalence, with incidences ranging from 3.5-12% (1-3). Longer term health implications are also coming to light, with a seven-fold increased risk of mothers developing type 2 diabetes later in life (4), whilst children of a GDM pregnancy are also at greater increased risk of type 2 diabetes and obesity (5).
Exercise has long been a beneficial therapy to managing type 2 diabetes, and a systematic review by Harrison et al (2016) (6) found similar improvements in glycaemic control in women diagnosed with GDM during pregnancy. Moderate intensity, cardiovascular or resistance (weight training) exercise performed a minimum 3 sessions per week safely lowered post meal and fasting glucose outcome measures, with no additional increase in adverse events (6).
Lower post meal blood glucose levels are linked to fewer maternal and neonatal complications (3) including excessive birth weight. In addition, up to 39% of women with GDM are unable to control blood glucose levels with diet modifications alone, further highlighting the benefits of exercise in the antenatal period.
If you have been diagnosed with gestational diabetes and would like more information on safe and effective exercise in the antenatal period contact our clinic to see Nicole our Exercise Physiologist and Physiotherapist.
Nicole also runs antenatal exercise classes at the clinic each Wednesday, enquire today to book in.
1. American Diabetes Association. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes care. 2013;36.67-74.
2. Artal R. Exercise: the alternative therapeutic intervention for gestational diabetes. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 2003;46:479-487.
3. Serlin DC, Lash RW. Diagnosis and management of gestational diabetes mellitus. Am Fam Physican. 2009;80:57-62
4. Bellamy L, Cases J-P, Hingorani AD, Williams D. Type 2 diabetes after gestational diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet. 2009;373:1773-1779.
5. Kral JG. Preventing and treating obesity in girls and young women to curb the epidemic. Obes Res. 2004;12:1539-1546.
6. Harrison AL, Shields N, Taylor NF, Frawley HC. Exercise improved glycaemic control in women diagnosed with gestational diabetes mellitus: a systematic review. J Physiother.2016.
Many people have heard of the rotator cuff in the shoulder but not many people actually know what it is. The rotator cuff is a group of muscles that help stabilise the shoulder during arm movements. The rotator cuff muscles are the supraspinatus, infraspinatus, subscapularis and teres minor and are seen in the picture below.
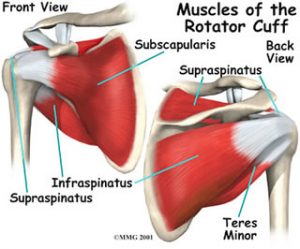
Rotator cuff tears can occur for multiple reasons. It could be caused from an accident or trauma to your shoulder or arm, or from a recurrent irritation to the tendons. It is very common in overhead athletes or older individuals. A tear can range from mild to severe and is usually dependent on how it happened.
Some of the symptoms associated with a rotator cuff tear include pain when lifting your arm out to the side or to the front, difficulty putting your arm behind your back and feeling weak in the shoulder and arm. You may also notice you’re unable to grip with that hand as easily as before.
A physio will assess how your shoulder and arm is moving as well as look at how strong the muscles around your shoulder are. There are several special tests a physio can also perform which will help diagnose your injury.
Treatment will involve looking at the biomechanics of your shoulder to find out why the impingement is occurring.
Sound like something you're experiencing? We can help! Give the clinic a call and we can help get you moving pain free.
Polycystic Ovarian syndrome (PCOS) is the most common hormonal disorder affecting up to 18% of reproductive aged women.
PCOS is closely linked with anovulatory infertility, increased insulin resistance, obesity, increased blood pressure and lipid profiles, depression and low self esteem, which can significantly impact one’s quality of life.
Lifestyle changes, including that of regular exercise is highly recommended for the management of PCOS and its associated symptoms. Exercise has been shown to have significant benefits on reproductive, body composition and biochemical health outcomes, including lowering insulin resistance and improving reproductive features of the condition.
The Australian guidelines for management of PCOS recommend at least 150 minutes of exercise per week, and it is important for participants to do exercise that they enjoy, to enhance adherence and long term exercise habits. Cardiovascular exercise for 30 minutes daily is highly encouraged as it can improve sensitivity to insulin, reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression, and enhance ovulation. Cardiovascular exercise is also frequently encouraged when doing IVF as it can boost reproductive success.
Strength or interval based resistance training is also another great exercise option for PCOS, as it can help to with weight loss and reducing abdominal circumferences. Metabolic health outcomes including weight loss have been shown to reduce PCOS symptoms, including lowering testosterone levels and improving insulin resistance.
If you’re keen to improve your health or are seeking additional advice to ensure you are exercising right for PCOS, contact our clinic to make a booking with our Exercise Physiologist and Physiotherapist Nicole for a tailored exercise program.
Olecranon bursitis is inflammation of the bursa that sits over the point of your elbow. This bursa is a fluid filled sac which allows your elbow to bend and straighten easier by letting the skin move easily over your elbow bones. When the bursa becomes inflamed movement of your elbow may become difficult or painful.
Olecranon bursitis can occur due to two reasons. The first and less common cause is from an infection in the body. The infection could be bacterial related or come from an insect bite or a cut/abrasion in the area. The more common cause of olecranon bursitis is a fall or blow to the elbow point.
The most common symptoms you will experience if you have olecranon bursitis is pain and notable swelling over the elbow point. If there is a lot of redness around your elbow and you are suffering from fevers this may indicate that your symptoms are coming from an infection. Usually you will still be able to move your elbow freely but touching the elbow point will be painful.
A thorough history of how your elbow pain and swelling began will aid the physiotherapist in identifying the cause of your olecranon bursitis.
Treatment will be determined based on the cause of your bursitis. If there is a current infection in your body, your physiotherapist will refer you to a medical professional for further review.
If this sounds like something that you may be experiencing, give the clinic a call and we can help you get back on track and move pain free.
As a dietitian, I spend a lot of time thinking - and talking - about guts. Mine, yours, everyones. And while it may not be the best dinner table conversation, it’s high time we all have a think about what our daily routine is doing to our insides. And, you can’t think about the gut without considering the 2kg of microorganisms which reside there, known as your gut microbiome.
Everyone has a unique mixture of gut microorganisms which help with digestion, vitamin B and K production and the immune system. It is affected by the environment, nutrition, stress, medications and disease.
If you’re interested in improving the health of your gut, you’ll have no doubt heard about probiotics and prebiotics. But what exactly are they?
Probiotics are live microorganisms which are found in foods. They assist the gut microbiome with digestion, including the production of vitamins and fatty acids, and are critical for normal immune system development. They also take up the prime real estate so harmful strains of bacteria have a tougher time taking over.
Prebiotics are non-digestible food ingredients that can increase the activity of probiotics. They act as the food for probiotics, which makes the probiotic more effective. They are mostly found in foods which are high in fibre.
Overall, taking a probiotic is a great step to take in increasing the friendly bacteria in your gut. Probiotics can assist with:
Taking probiotics alongside antibiotics reduces the risk of diarrhoea. Strains which have evidence about being successful include Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG, L.acidophilus (found in yoghurt), L. caseii and Saccharomyces boulardii (a yeast).
Some studies that show benefit from probiotics reducing symptoms of IBS but there is more research in this area needed to work out strain and dosage. IBS symptoms are very individualised so treatment would vary.
There are various mechanisms where probiotics may play a role in reducing illness severity or duration, however there is not enough evidence from large, well designed, dependant studies to prove this.
Some studies have found taking probiotics while travelling can reduce the risk of travellers’ diarrhoea.
To summarise, probiotics have a lot of potential to have some very interesting effects on our health. The issue that we currently face is that there are a lot of different strains and each product varies massively, making it difficult for professionals to make accurate recommendations.
Hopefully as interest increases in this area, more evidence will emerge as to exactly which probiotic we should be taking.
The head of your arm bone sits in a shallow socket formed by your shoulder blade known as the glenoid cavity. This shallow socket is quite small and the labrum helps deepen the cavity and provide support to the head of your arm bone. This support helps stabilise the shoulder joint further and maintains the head of your arm bone in the cavity. The labrum is made of fibrous cartilage tissue and although it is very strong, it is susceptible to injury.
Labral lesions can be caused by several things as with other shoulder injuries. Common causes of a labral lesion can include; falling on an outstretched hand, a shoulder dislocation, strong biceps contraction or repetitive movements.
Symptoms of a labral tear can include hearing a clicking noise or feeling like your shoulder is catching on something when you move it. You may also experience a vague pain on the front or top of your shoulder which will worsen when you lift your arm up.
A physio will assess how your shoulder and arm is moving as well as look at how strong the muscles around your shoulder are. There are several special tests a physio can also perform which will help diagnose your injury.
Treatment will involve looking at the biomechanics of your shoulder to find out why the impingement is occurring.
If this sounds like something that you may be experiencing, give the clinic a call and we can help you identify the issue and treat it, quickly and professionally.
In the third of our Injuries Unpacked series, we’re looking at elbow ligament injury.
The elbow has three main ligaments that help keep it stable during movement. The most common ligament to be injured is the medial collateral ligament that lies on the inside of your elbow.
Elbow ligament injuries can occur due to hyperextension of your elbow after a fall or the application of a strong force causing your lower arm to bend or twist outward. The medial collateral ligament is most commonly damaged through repetitive stress to the inner elbow through movement. This usually occurs in sports involving repetitive throwing or overhead movements such as baseball, volleyball or tennis.
Pain over the particular ligament which is damaged is a common symptom in elbow ligament conditions both during activity and when touched. You may also find it difficult to perform activities where your arm is up over your head and your grip strength may become reduced.
A physio will assess where exactly your pain is and analyse what activities are causing your pain. From a thorough history and physical examination, diagnosis of which ligament is causing your problems will be made. There are several special tests a physio can also perform which will help diagnose your injury.
Usually a period of rest from the aggravating activity and a personalised physiotherapy program will be enough to help improve your symptoms.
If this sounds like something that you may be experiencing, give the clinic a call and we can help you get back on track.